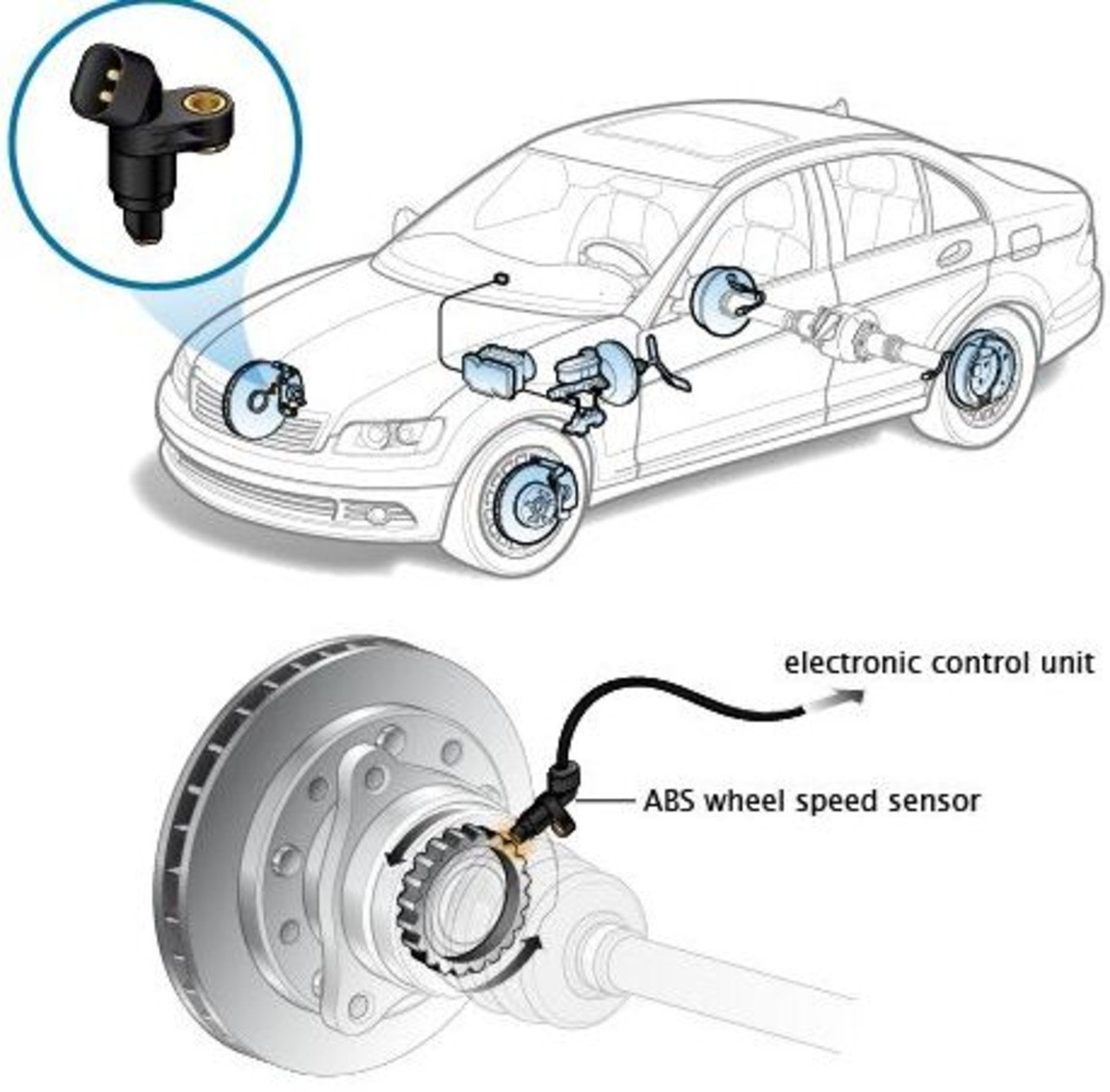
The speed sensor is a device that transmits the vehicle’s speed to the speedometer. Operating your car’s gearbox and cruise control systems is essential.
This post will define a speed sensor and explain its working. Afterward, we’ll discuss how much it costs to replace it and what signs indicate it’s time to do so.
Finally, we’ll review how many types of speed sensors are available and how you can maintain your speed sensor for a long time.
What Is A Speed Sensor?
Connected to the gearbox, a vehicle’s speed sensor relays information about the vehicle’s speed to the vehicle’s central processing unit (CPU). It is also called:
- Transmission speed sensor
- A wheel speed sensor
- Output shaft speed sensor
Various sensors, such as those for temperature, crankshaft position, pressure, etc. make up the engine sensor control, including the speed sensor or the ABS sensor. As a great thing, specific sensors can figure out which way anything is facing.
Once Installed, How Does It Work Properly?
The sensor in your car can tell you how fast the gears are turning since it can read the rotational speed of the gearbox. When an inductive sensor detects a change in magnetic flux, an analog signal or low-voltage square wave signal is generated, representing this speed change. The sensor sends the signal to the automobile’s ECUs.
The electronic control units (ECUs) then utilize this square wave signal to fine-tune various aspects of your vehicle, including the speedometer, throttle, ignition, brakes, and gearbox.
The sensor in your automobile may also be used by cruise control and traction control systems. An automobile with this feature would have helped keep a steady pace.
These sensors are a common addition for equipment that can’t detect speed with any physical touch.
The Different Kinds Of Speed Sensors
The many sensor types include:
· Sensor Using a Reed Switch
A magnet and reed switch make up this sensor, speedometer wire activates it.
When the magnet rotates, it toggles the reed switch on and off around four times. This enables the measurement of vehicle speed through the computation of pulses per second.
· Sensor, Hall Effect
To generate a magnetic field (magnetic flux) and an associated voltage, a Hall effect sensor uses a moving reluctator in opposition to the hall sensor. The ABS’s processing units receive this voltage and use it to do their work. The anti-lock braking system determines the rate of speed.
· Active Sensor
A voltage is required for the operation of the active sensor. This digital signal is subsequently sent to the ABS controller.
An active sensor can detect the wheels’ direction and operates most effectively at low speeds.
· Passive Sensor
Passive sensors include inductive sensors and variable-reluctance magnet sensors (VR sensors). You can use these sensors with the available power and avoid extra power. The data output is sent to the ABS by sensing the speed at which the wheels spin.
Signs Of A Faulty Speed Sensor
A properly functioning speed sensor is essential for safety and convenience features on your vehicle, including the accuracy of the speedometer measurement, anti-lock brakes, spark ignition, gearbox, and cruise control.
You should check the sensor in your car if you encounter any of the following while driving:
1. Nasty Gear Shifts
The engine control module can only correctly manage gear changes in the gearbox with solid input from the sensor.
So, what exactly does it lead to?
- Abrupt gear changes and transmission shift time might be affected by the PCM.
- A defective sensor in an automatic transmission vehicle may also severely harm the actual gear tooth shape and other interior parts, including hydraulic lines, cylinder bodies, and more.
- If your transmission is acting up, you should get a checkup soon to be safe.
2. The Check Engine Light Flashes
There are several potential causes for the flashing of the Check Engine Light on the dashboard of your vehicle, including:
- A malfunctioning spark plug or ignition coil
- Problems with the fuel injector
- Incorrect temperature setting due to a broken thermostat
- Tires with inadequate air
A faulty transmission sensor, though, may cause the same thing to happen.
There is a risk that your vehicle’s electronic control unit won’t pick up the signal from the transmission speed sensor if the sensor is broken. Additionally, this malfunction may cause your vehicle’s “engine light” to come on.
Remember that other warning lights, such as anti-lock brakes or traction control lights, might also point to its problems.
3. The Speedometer Gives Wildly Varying Readings
Most modern automobiles use information from a sensor in the wheel to accurately display the vehicle’s speed. The accuracy of a speedometer may be affected by a broken sensor.
It also can show 0 readings on the speedometer. In other words, your automobile won’t suddenly cease functioning and become undrivable.
But if your car’s speedometer is broken, you won’t know how fast you travel, which might be dangerous.
4. Broken Cruise Control
The system for cruise control in most vehicles receives activation signals from the transmission speed sensor.
Thus, you will likely not be able to use the cruise control feature of your vehicle if its sensor malfunctions.
Why?
Your car’s powertrain control module (PCM) will often deactivate the cruise control system if it does not receive a valid signal from its speed sensor.
This is done because, with information from the transmission sensor, cruise control can keep the car moving at a consistent pace. Learn more about How to relocate and replace the camshaft sensor.
What is the average price to replace the camshaft sensor?
The price of a new speed sensor is going to vary based on the kind of car you have. Whether an active sensor, VR sensor, optical sensor, magnetic field sensor (Hall effect sensor), or any other kind of sensor is employed is also a factor.
To counter this, replacing a sensor often costs little money and you have to replace the brake lines or the main cylinder.
Replacement of the vehicle speed sensor, whether a hall sensor or another sort, would likely cost you between $200 and $400.
FAQs
Why is there a need for both an output and an input speed sensor?
Typically, two transmission sensors provide information to the powertrain control module. The input speed sensor tracks the input shaft’s rotational velocity inside the transmission. The output speed sensor is the second kind of sensor that tracks the output shaft’s rotational velocity.
Where is the speed sensor located?
Typically, it will be fitted into the shaft of a wheel or friction motor from the side.
What happens when a wheel speed sensor goes bad?
A malfunctioning wheel speed sensor will not alert the engine control unit. You risk losing control of your car and crashing if the ABS cannot activate.
Conclusion
Speed sensor tells and manages the speed of your vehicle, and there are different types of them. It location is near the crankshaft or the output sensor of the transmission. However, much like brake pads, your sensor’s lifespan highly depends on how you typically drive. The sensor won’t survive as long if constantly subjected to harsh elements like road salt and other chemicals. Thus, it would help if you replace it to avoid significant damage to your vehicle.