There are quite a lot of Immunotherapy Success Stories in todays world. Did you know what the success rate of immunotherapy is?
Immunotherapy medications are more effective in some malignancies than others, and while they might be a lifesaver for some patients, they do not work for everyone. The overall response rate is around 15% to 20%.
The term “immunotherapy” refers to a biologic treatment that utilizes your immune system to combat cancer. Although it is more effective against certain kinds of cancer than other types, it can be utilized in general ways or to target specific cancerous cells.
CRISPR, artificial intelligence, telemedicine, the Infinium Assay, cryo-electron microscopy, and robotic surgery are some technologies and breakthroughs that assist in the fight against cancer.
CRISPR Technology
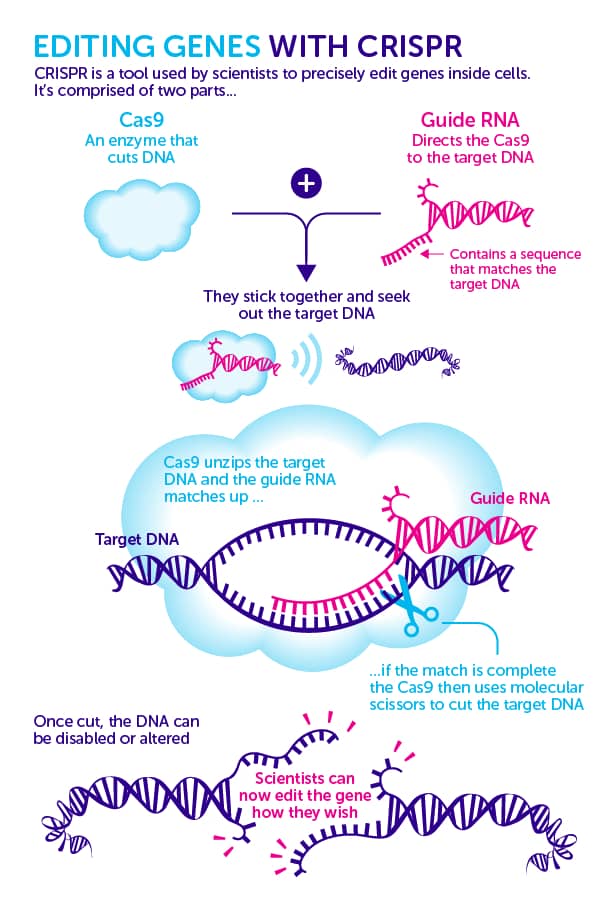
CRISPR is a sophisticated genome-editing technique that allows scientists to easily change DNA sequences and gene functions. It offers a wide range of potential uses, including the correction of genetic abnormalities, the treatment and prevention of illness, and enhancing crop growth and resilience.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence In Cancer
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is all over the place. Personal digital assistants are everywhere:
- They answer our questions.
- Robo-advisors make trades on stocks on our behalf.
- Driverless vehicles will eventually take us to wherever we’d like to travel.
AI has impacted our lives and its application is increasing in biomedical research and health care, including across all aspects of cancer research. The applications that could be made for AI are endless.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence is a computer that performs tasks typically related to human intelligence. Humans program or code machines to behave, reason, think, and learn. A model or algorithm is an algorithm or model is the code that instructs the computer on how to act or reason and also learn.
Machine Learning (ML)
Machine learning is a form of AI that isn’t designed to accomplish a specific task but instead learns repeatedly to predict or make decisions. The more information an ML model has to deal with, the more data it is exposed to, and the better it performs over time.
Deep Learning (DL)
Deep learning is an aspect of ML that employs artificial neural networks modeled on how the human brain processes data to make sense of massive quantities of data. A well-designed and trained DL model can complete classification tasks and create predictions with high precision, often exceeding human expert performance.
AI excels in recognizing patterns that are present in huge amounts of data, identifying relationships between intricate features within the data, as well as identifying features in the data (including images) that aren’t recognized in the brain of a human.
It has already yielded outcomes in Radiology where doctors utilize computer systems to analyze images in a rapid manner. Which allows radiologists to focus their efforts on areas where their technical expertise is crucial. For instance, in the past, it was announced. The Food and Drug Administration approved the first AI-based program to analyze images quickly and assist doctors in detecting breast cancer by screening mammograms.
The use of AI technology in cancer treatment can improve the speed and accuracy of diagnosis, support medical decision-making and contribute to improved health outcomes. AI-guided medical care could be a significant factor in reducing health disparities, specifically in areas with limited resources. NCI will invest in research and development in developing infrastructure and providing training to the workforce to help reach these goals and more.
Telemedicine in the field of Cancer Care
Telemedicine makes use of telecommunications technology to deliver health services to people who have limited access to healthcare. It has been evaluated in various clinical settings and has demonstrated at least the same quality as in-person health care and high patient and healthcare professional satisfaction levels.
Teleoncology has been proven to enhance access to healthcare and lower healthcare costs. Teleconsultations may be offered in either synchronous or asynchronous, or mixed format. Examples of successful teleoncology services include cancer telegenetics, bundles of teleapplications related to cancer, remote chemotherapy monitoring and treatment of symptoms, survivorship and palliative treatment, as well as methods to improve the number of cancer clinical trials.
Telepathology is a crucial aspect of cancer treatment and can be performed synchronously or simultaneously for both cytology and the diagnosis of tissue. Mobile applications aid in managing symptoms, lifestyle changes, and adherence to medication as a tool to provide care at home. Telemedicine can assist oncologists by providing interactive tele-education.
Teleoncology practices should be in line with the standards of professional practice in person, which includes documentation integrated into the patient’s electronic health record. For that sort of treatment, there are extremely few Immunotherapy Success Stories.
Cryo-Electron Microscopy
Cryo-electron microscope (cryo-EM) describes a variety of methods, including single particle analysis and cryo-tomography. It is used to gather high-resolution structural data for biological systems.
In cryo-EM, the sample solutions are quickly frozen, which prevents the formation of crystalline ice, and conserves the natural shape of the specimens. Single-particle analysis results in the formation of a suspension of proteins placed at different angles within the frozen.
The cryo-transmission electron microscope (cryo-TEM) is then utilized to visualize the proteins, creating many thousands of 2D projected images from the specimen. These projections are then combined into a 3D high-resolution image of protein. With modern electron detectors and analysis software, Atomic resolution is achievable and becoming more affordable.
Scientists are now using cryo-EM to help in cancer research, which has led to the development of “structural oncology,” an emerging field that hopes to apply concepts of structural biology in fighting cancer.
Robotic Surgery for Cancer
For certain types of cancer, open surgery might not be the ideal option. Through robotic surgery, specially trained surgeons employ robotics, such as tiny surgical instruments as well as an electronic console, to treat cancer in a patient.
Robotic surgery is typically performed using a laparoscope. During surgery, the surgeon inserts a tiny instrument with a bright and small camera, referred to as a laparoscope, through minor cut marks on the patient’s skin. The laparoscope relays images to a video monitor, so the surgeon can observe inside the body without making larger cuts.
Robotic surgery is also referred to as robot-assisted surgery. The 3-D imaging and robot-assisted technology permit surgeons to perform intricate surgeries with greater accuracy than traditional techniques.
In the general sense, doctors can achieve two primary goals when performing cancer surgery:
- Combating cancer effectively as possible.
- Ensuring that the patient’s recovery is as quick and as smooth as it is.
The type and stage of cancer and their prognosis determine the objectives for the procedure.
Based on your specific situation, the possible outcomes for surgery may include:
- The cure for cancer is by eliminating the cancerous.
- The reduction (debulking) the size of the tumor in preparation for chemotherapy or any other treatment.
- The treatment of the loss of feeling or pain.
Your surgeon will determine if robotic surgery is appropriate for your specific cancer. If yes, your surgeon might recommend robotic surgery instead of open surgery.
Different Types Of Immunotherapy
Monoclonal Antibody and Other Tumor-Agnostic Therapies
Also called therapeutic antibodies monoclonal antibodies are human-made protein molecules that attach themselves to certain targets on cancerous cells. The cancer cells may be killed in a direct manner, but can also mark cancerous cells for recognition and attacked by immune cells.
Non-Specific Immunotherapies
Non-specific immunotherapies are employed when targeted therapies aren’t required. In this situation the non-specific treatment is employed to increase the overall immune system to ensure that it is able to fight all cancerous cells.
The Treatment for Oncolytic Viruses
These cancerous cells can be more prone to infection, and certain viruses are modified to be able to directly attack cancerous cells. The virus can penetrate the cells and cause the cells to die.
T-Cell Therapy
In t-cell therapy your immune cells are harvested and utilized to treat cancer. Although this therapy is typically used for patients suffering from blood cancers but it can also be used to treat solid tumors, and further developments are being made for its application constantly. We also find some Immunotherapy Success Stories from that kind of treatment. In T-cell therapy, the success rate is about 30% to 40%.
Cancer Vaccines
In the same way, Vaccines can increase your body’s immune response to certain pathogens. Vaccines are also used to enhance your immunity against cancer.
They include cytokines that are proteins that play essential to the body’s immune system and Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG), a kind of bacteria used to treat bladder cancer. There are very few Immunotherapy Success Stories for that type of treatment, and overall response rates are about 15 to 20%.
What Is Ipilimumab And How Does It Work?
Ipilimumab is an immunotherapy drug used to treat cancer. Ipilimumab may be used to treat Melanoma resistant to surgery and Melanoma has spread to another section of the body (advanced Melanoma). Another medicine called nivolumab was used to treat advanced kidney cancer (renal cell carcinoma).
Immunotherapy Success Stories for Ipilimumab treatment is 20 Percent, roughly 20% of patients being alive years later.
Mesothelioma Immunotherapy
Mesothelioma immunotherapy is a type of treatment that utilises drugs to aid the body’s immune system in fighting malignant mesothelioma. Immunotherapy for mesothelioma seeks to train the body to detect dangerous cancer cells. Prevent cancer from lowering immune response and assist the immune system in killing cancer cells.
A mesothelioma patient’s life expectancy ranges from 12 to 21 months following diagnosis. Depending on the stage of cancer, the location of the tumour, and the kind of mesothelioma cell, some mesothelioma patients may live longer and healthier lives.
Immunotherapy Against Chemotherapy
Immunotherapy is a method of empowering the immune system of your body to combat the cancerous process, chemotherapy uses drugs to destroy rapidly growing cancer cells. However, chemotherapy isn’t a discriminatory treatment as all cells that are fast-growing such as healthy digestive tract, hair follicles and blood cells are also targeted.
Because chemotherapy shrinks tumors right away, In some immunotherapy success stories we notice usually is slower to show outcomes; chemo tends to be employed in the most urgent, advanced treatment options for cancer.
The Side Effects of Immunotherapy
The adverse effects of immunotherapy are typically due to the overactive immunity system. It is possible that they differ based on your overall health prior to treatment as well as the stage and type of cancer, as well as the type of treatment you’re receiving.
The most common side effects include:
- Fatigue
- The cough and dyspnea (resembles pneumonia)
- A decrease in appetite
- Diarrhea
- Weight loss
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Rash
- Blisters, and possibly the appearance of a eruption of rashes
- Headache
- Insomnia
Risky side effects may also happen immediately, or even for as long as two years after treatment. This could include:
- Lung inflammation
- Liver inflammation
- The colon is inflamed
- Endocrine disruption
- Brain swelling
- Kidney problems, including kidney failure
- Infections that are severe
- An allergic reaction severe to the infusions
Because some of the adverse effects of immunotherapy can be life-threatening. It’s important to notify a physician immediately if you experience one of these.
Immunotherapy Procedure Details
Treatments are offered regularly, weekly or every month. Under this kind of treatment, the stage and type of cancer and how the body responds to treatment.
Certain immunotherapy treatments can be delivered in cycles. Which means intervals between treatments so that your body can recuperate and regenerate healthy cells.
The treatment also involves regular visits to the doctor for tests to confirm that they are functioning and to check your health. This can include physical tests, as along with blood tests and other scans.
Contact Us to Discuss Immunotherapy
In the case of the diagnosis of cancer early and top-quality treatment options are crucial to increase your chances of surviving. In Intermountain Healthcare, our goal is to provide only the highest quality Oncology/Hematology treatments possible to ensure you can have the highest chance of beating this horrible disease. With clinics and doctors conveniently located across Southern Nevada along with an simple appointment scheduling system You can be at ease knowing that we’re accessible for all of your healthcare requirements.
Feature Image By pexels.com





