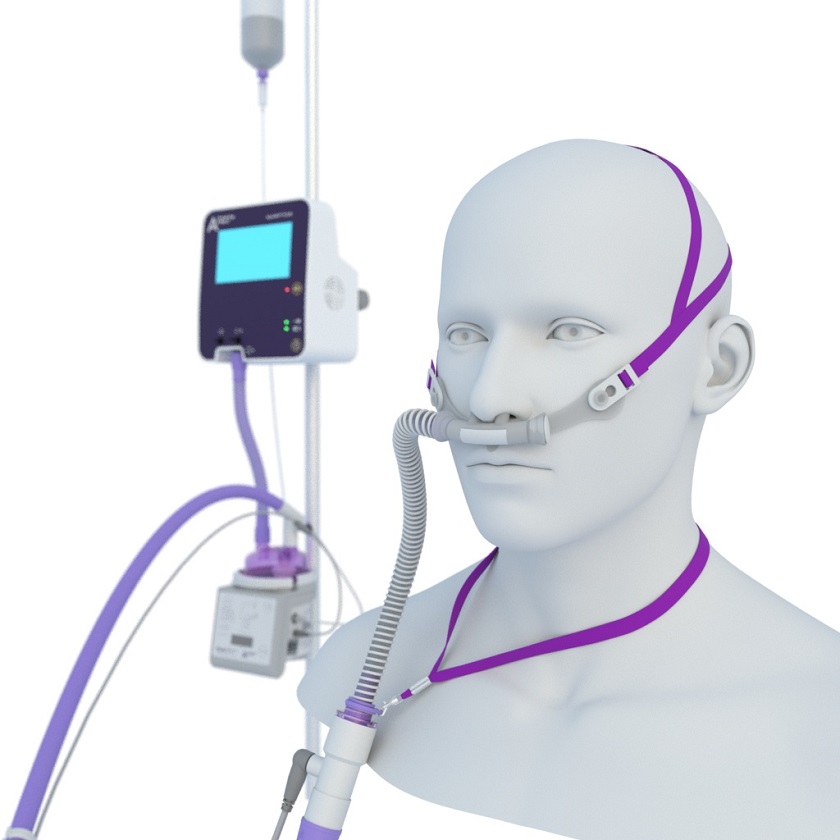
High flow oxygen devices are medical devices that are designed to deliver oxygen to patients with respiratory distress. These devices are typically used in emergency situations, such as in an ambulance, or in a hospital setting when a patient is unable to adequately breathe on their own. These devices work by increasing the flow rate of oxygen to the patient, which in turn increases the amount of oxygen that is delivered to the lungs.
There are several different types of devices accessible, each with its own individual set of benefits and disadvantages.
Different Types of High Flow Oxygen Devices
- The most common type of high-flow oxygen therapy is a nasal cannula. This device consists of a flexible tube that is placed in the nostrils, with a connector that attaches to an oxygen source. The flow rate of oxygen delivered through a high flow nasal cannula can adjust to meet the patient’s needs. It allows for the precise delivery of oxygen to the lungs.
- Another type is a non-invasive ventilation (NIV) mask. This type of device is similar to a traditional high-flow oxygen mask, but it is designed to deliver higher flow rates of oxygen to the patient. The NIV mask typically features a one-way valve that allows air to flow in, but not out. It helps to reduce resistance and increase the flow rate of oxygen to the lungs. NIV masks can be particularly useful for patients with severe respiratory distress, as they are able to deliver higher flow rates of oxygen than other types of oxygen devices.
- A third type of high flow oxygen device is known as a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine. This type of device is designed to deliver a constant flow of pressurized air to the patient, which helps to keep the airways open and prevent collapse. CPAP machines are commonly used in hospitals and other medical facilities to treat patients with sleep apnea, but they can also use in emergency situations to treat patients with severe respiratory distress.
Types of Oxygen Devices
In addition to these three main types of devices, there are also other types of oxygen delivery systems available. It includes bi-level positive airway pressure (BiPAP) machines and oxygen tents. Each of these devices has its own unique set of benefits and drawbacks. The choice of device will depend on the specific needs of the patient and the situation.
The use of high flow oxygen devices has been shown to be effective in treating patients with respiratory distress. When used appropriately, these devices can help to improve the patient’s oxygenation. It reduces the risk of hypoxia, and improves their overall respiratory function. These devices can also help to reduce the risk of respiratory failure, which can be a life-threatening condition if not treated promptly.
Potential Threats Related Of High Flow Oxygen Devices
Although, there are as well some potential threats related to the use of these devices. For example, high flow oxygen devices can increase the risk of carbon dioxide retention, which can lead to hypercapnia. Additionally, the use of these devices can also increase the risk of nosocomial infections, as they can increase the exposure of the patient to bacteria and other infectious agents.
Despite these potential risks, high-flow oxygen for covid patients continues to play an important role in the treatment of patients with respiratory distress. By providing a reliable and effective means of delivering oxygen to the lungs. These devices can help to improve the patient’s outcomes and reduce the risk of serious complications. Whether in an emergency setting or in a hospital setting, these devices are an important tool in the management of patients with respiratory distress.
On the other hand, when we talk about high-flow oxygen devices vs ventilators there is a high difference.
High flow oxygen refers to a delivery system that provides a high flow of oxygen to a patient. The oxygen is delivered through a nasal cannula, which is a thin tube that fits into the nostrils, or through a full face mask.
A ventilator, on the other hand, is a machine that mechanically assists a patient in breathing. It is used to provide breathing support to patients who are unable to breathe adequately on their own, such as those with severe respiratory failure or who have undergone major surgery that affects their ability to breathe.
What is considered a high flow device?
A high-flow device refers to a device or system that has the ability to flow. It circulates a large amount of fluid, gas, or air per unit of time. The definition of high flow can vary depending on the context, but it is typically characterized by a flow rate. It exceeds the normal or expected range for a given system or application.
In medical applications, a high flow device refers to a device that delivers oxygen. The other gases to a patient at a flow rate that exceeds the patient’s resting minute ventilation. This type of device is commonly used in the treatment of respiratory distress. The other medical conditions require increased oxygenation.
In engineering applications, a high flow device refers to a system or component that can handle a high volume of fluid or gas with minimal pressure drop. This type of device can often use in industrial, commercial, and residential applications. The high flow rates are required for heating, cooling, or other purposes.
Generally, the term high flow is parallel and based on particular conditions and applications.
What is the difference between high flow and low flow oxygen devices?
High-flow oxygen devices and low-flow oxygen devices refer to the rate at which oxygen is delivered to a patient through an oxygen delivery system. The major change between the two consists of the flow rate of oxygen.
- Low flow oxygen devices deliver a low flow rate of oxygen, typically between 1-5 liters per minute, which is sufficient for most people at rest. These devices include nasal cannulas and simple oxygen masks. Low-flow oxygen devices are suitable for patients with stable respiratory conditions who require supplemental oxygen to maintain their oxygen saturation levels.
- High flow oxygen devices, on the other hand, deliver a high flow rate of oxygen. It is typically greater than 5 liters per minute. These devices are used for patients who require higher oxygen flow rates to compensate for increased oxygen demand or decreased oxygen supply. These devices consist of high flow continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), non-invasive positive pressure ventilation (NPPV), and nasal cannulas.
Pros of High Flow Oxygen Devices
Increased Oxygenation
High flow devices can deliver high flow rates of oxygen. It can be beneficial for patients with respiratory distress or hypoxemia.
Improved Comfort
High flow devices can provide humidified and heated air. It can more comfortable for patients when compared to traditional oxygen delivery methods.
Reduced Dead Space
High flow devices can reduce the amount of dead space in the airway. It can prevent rebreathing of carbon dioxide and improve respiratory function.
Minimal Patient Interference
High flow devices can be less intrusive for patients, allowing for greater freedom of movement and reduced stress.
Cons of High Flow Oxygen Devices
Cost
High flow devices can more expensive when compared to traditional oxygen delivery methods. It can present a challenge for some healthcare facilities.
Maintenance Requirements
High flow devices require frequent cleaning and maintenance, which can be time-consuming and may increase the risk of infection.
Limited Availability
High flow devices may not be available in all healthcare settings. Particularly in low-resource areas where access to advanced medical equipment is limited.
Potential Complications
High flow devices can cause nasal or oral dryness, nasal trauma, or other complications, particularly in patients with underlying medical conditions.
Final verdict
In conclusion, high flow oxygen devices are a system that can use for giving oxygen to an affected person. This tube is placed down in the nostrils. Oxygen flows through the tube and helps the patient to breathe easily. It reduces the difficulties which the affected person is facing in breathing.